As-Built Services A Comprehensive Guide
As-built services – As-built services provide a detailed record of a project’s final state, crucial for everything from construction to manufacturing. This guide delves into the specifics, from defining the core concept to exploring its various applications across different industries.
We’ll examine the key characteristics that distinguish as-built services from other service types, analyzing their scope and application in construction, engineering, and manufacturing. We’ll also cover the essential elements and components of as-built services, detailing the documentation, procedures, and benefits they offer. Finally, we’ll discuss potential challenges, future trends, and the critical role of accurate data and documentation.
Defining As-Built Services
Source: teamzelus.com
As-built services represent a crucial step in any project, particularly in construction and engineering. They document the actual, final state of a project, differing significantly from the initial design plans. This detailed record ensures that future maintenance, modifications, or expansions are informed by the precise, real-world execution of the project.
As-built services meticulously capture the physical attributes of a project, providing a comprehensive record for stakeholders. This accuracy is critical in preventing costly errors and ensuring smooth future operations. It’s more than just a drawing; it’s a detailed account of the built environment.
Characteristics of As-Built Services
As-built services possess specific characteristics that distinguish them from other service types. They are:
- Detailed and Accurate: These services offer a precise representation of the constructed project, differing from initial design documents. The details of materials used, dimensions, and locations are meticulously recorded. For instance, if a project involves plumbing, the as-built services will accurately depict the precise location of each pipe and fitting as installed, not as originally planned.
- Project-Specific: Each as-built service is tailored to a particular project. This specificity ensures that the documentation directly corresponds to the unique physical realities of the completed project.
- Post-Construction: As-built services are created after the construction phase is complete. They document the physical reality of the built environment, not the initial design.
- Comprehensive Documentation: As-built services are more than just drawings. They can include detailed specifications, material lists, and other supporting documentation that accurately capture the final configuration of the project.
Types of As-Built Services
A wide range of services fall under the umbrella of “as-built.” These services encompass different aspects of a project, reflecting the complexity of modern construction and engineering projects.
- Architectural As-Built Drawings: These encompass the final floor plans, elevations, sections, and details of a building, including any deviations from the initial design. For example, if a wall was moved slightly during construction, the architectural as-built drawing will reflect that precise location.
- Engineering As-Built Drawings: These drawings cover the detailed layouts of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems (MEP). These as-built drawings accurately depict the final positions of pipes, wires, and conduits.
- Site As-Built Surveys: These services document the actual site conditions after construction, including features like grading, utility locations, and landscaping. This is critical for future development or maintenance, as it ensures the record reflects the real-world site configuration.
- As-Built Specifications: This documentation provides the detailed specifications of materials used in the construction. This is important for future maintenance and replacement, as it ensures that the right materials are used for repairs.
Comparison with Other Service Types
| Feature | As-Built Services | Other Services (e.g., Design Services) |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Post-construction | Pre-construction |
| Focus | Actual built environment | Conceptual design |
| Accuracy | Precise representation of the final product | Conceptual representation of the project |
| Purpose | Future reference, maintenance, modifications | Planning and development |
Scope and Application of As-Built Services: As-Built Services
As-built services play a crucial role in various industries by providing detailed records of completed projects. These records, often in the form of digital documentation, are invaluable for future reference, modifications, and maintenance. They act as a precise blueprint of the actual constructed asset, differing from the original design documents.
As-built services extend beyond just capturing physical dimensions. They incorporate detailed information about materials used, specifications, and any deviations from the initial plan. This comprehensive data ensures a complete understanding of the project’s execution, aiding in future decisions.
Industries Employing As-Built Services
As-built services are widely used across numerous industries. Their utility extends beyond construction, impacting engineering and manufacturing processes. Accurate records of completed projects are vital for ongoing operations and potential expansions.
Typical Use Cases for As-Built Services
As-built services have numerous practical applications. These include verifying compliance with regulations, facilitating maintenance and repairs, and supporting future expansions or modifications. They serve as a single source of truth for all project details.
Applications in Construction
Construction projects often benefit from as-built services. These services are vital for documenting site conditions, material choices, and structural details. They assist in future modifications and repairs by providing detailed information about the existing infrastructure. Accurate as-built drawings are essential for efficient project management, allowing for better coordination among teams and stakeholders. Furthermore, these records can minimize conflicts during future construction phases.
Applications in Engineering
As-built services are equally valuable in engineering projects. They capture the specifics of equipment installations, pipeline routes, and electrical layouts. These detailed records are critical for maintaining and upgrading complex systems. Engineers can rely on as-built data to quickly identify and resolve potential issues. Examples include updating schematics for industrial equipment and facilitating efficient maintenance routines.
Applications in Manufacturing
Manufacturing also utilizes as-built services to maintain detailed records of equipment, tooling, and production lines. These services are valuable for troubleshooting, optimizing production processes, and facilitating upgrades. They help maintain equipment efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve productivity.
Successful Applications of As-Built Services
Numerous successful implementations showcase the effectiveness of as-built services. One example involves a large-scale power plant upgrade. The as-built data facilitated the integration of new equipment, reducing downtime and ensuring smooth operations. Another example is a manufacturing facility’s refurbishment. The as-built documentation allowed for the efficient relocation of equipment, saving significant time and resources.
Key Applications and Benefits of As-Built Services
| Sector | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Documenting site conditions, material choices, and structural details; facilitating modifications and repairs | Improved project management, minimized conflicts, enhanced efficiency, and reduced rework. |
| Engineering | Capturing equipment installations, pipeline routes, and electrical layouts; supporting maintenance and upgrades. | Simplified maintenance, quicker troubleshooting, improved system efficiency, enhanced planning for expansions |
| Manufacturing | Maintaining records of equipment, tooling, and production lines; optimizing production processes, facilitating upgrades | Improved equipment efficiency, reduced downtime, optimized production, streamlined troubleshooting |
Key Elements and Components
Source: co.uk
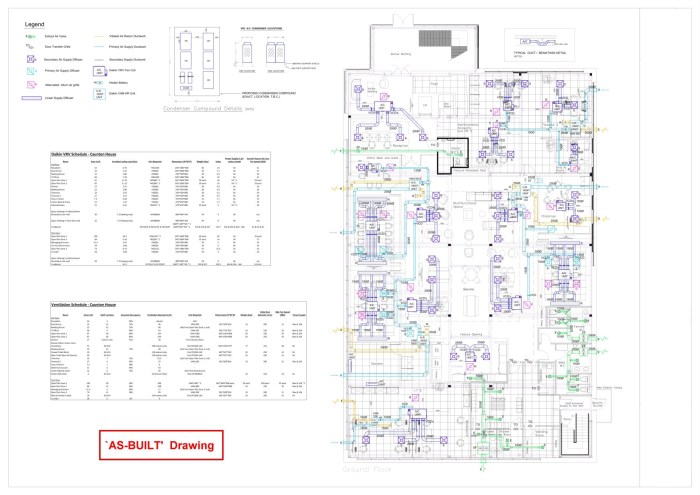
As-built services are crucial for documenting and understanding the final stage of a project. They provide a detailed record of everything constructed, from the precise location of pipes and wiring to the exact specifications of equipment. This detailed record is essential for future maintenance, modifications, and understanding of the project’s execution.
The core of as-built services lies in the comprehensive documentation that captures the project’s physical reality. This documentation serves as a blueprint for future work, facilitating efficient and accurate updates, maintenance, and potential expansions. It also helps avoid costly errors and ensures that future projects can benefit from lessons learned.
Essential Components
The foundation of any as-built service rests on a few key components. These elements ensure accuracy, completeness, and usability for future reference. A detailed breakdown of these components is essential for effective management and implementation of as-built services.
- Measured Data: This encompasses precise measurements of all constructed elements, including dimensions, locations, and specifications. This data forms the backbone of the as-built documentation, enabling accurate representation of the final project. For instance, precise coordinates for utility lines or the exact height of a building structure are examples of measured data.
- As-Built Drawings: These are technical drawings that visually depict the completed project. They are essential for conveying the layout, specifications, and interconnections of different systems. These drawings typically include detailed schematics, plans, and sections of the built structure.
- Material Specifications: A complete list of materials used, along with their corresponding specifications, is crucial for maintenance and future repairs. This section includes details like material type, grade, and any unique characteristics that are essential for understanding the project’s components.
- Photographs and/or 3D Models: Visual representations of the completed project are invaluable for understanding the physical arrangement of the structures and components. Photographs and 3D models can be incorporated to provide a holistic view, capturing the spatial relationships between various parts of the construction.
Deliverables and Outputs
As-built services generate various deliverables, each playing a specific role in the project’s lifecycle. Understanding these outputs is critical for efficient project management and future utilization of the information.
- As-Built Documents: These documents collate all the information mentioned above into a comprehensive package. This includes drawings, specifications, measured data, and any relevant supporting information. This package provides a single source of truth for the project.
- Data Files: Electronic versions of the as-built data, such as CAD files, spreadsheets, or databases, allow for easy access and modification. Data files also enable integration with other systems, improving the efficiency of data management.
- Project Reports: Summary reports provide an overview of the project’s completion. These reports can include cost summaries, timelines, and a detailed account of the construction process.
Documentation
Thorough documentation is vital for the long-term usability and maintainability of as-built services. Properly structured documentation ensures that all relevant information is readily accessible.
- Metadata: Metadata describes the as-built data, providing context and aiding in efficient search and retrieval. This includes details like the date of creation, the author, and a description of the data.
- Version Control: Maintaining different versions of the documentation ensures that the most current information is readily available. This is particularly important in projects with iterative design or modification.
- Index and Cross-Referencing: A detailed index and cross-referencing system allows for easy navigation and retrieval of specific information. This is especially useful for complex projects where numerous elements are involved.
Summary Table
This table summarizes the components and their roles in an as-built service.
| Component | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Measured Data | Precise measurements of project elements. | Forms the basis for accuracy and completeness. |
| As-Built Drawings | Visual representation of the project. | Provides a clear and understandable layout. |
| Material Specifications | Detailed information on materials used. | Essential for maintenance and future repairs. |
| Photographs/3D Models | Visual representation of the built structure. | Provides a holistic view of the project. |
Process and Procedures
Delivering as-built services involves a structured process to ensure accuracy, completeness, and adherence to specifications. This process encompasses data gathering, documentation creation, verification, and quality control, all meticulously managed to produce reliable and usable as-built deliverables.
The process for as-built services is crucial for post-project analysis and future project planning. Thorough documentation and accurate data are vital for understanding the actual construction or implementation, enabling better cost estimations and risk assessment for future projects.
Typical Delivery Process
The typical process for delivering as-built services usually follows a phased approach. The initial steps focus on defining the scope and gathering necessary data, followed by thorough documentation, verification, and quality control. The final phase involves finalizing the documentation and making it accessible to stakeholders.
Data Gathering and Documentation
Gathering accurate data is paramount to creating a reliable as-built document. This often involves a combination of field surveys, review of existing plans and specifications, and analysis of project records. The gathered information must be precisely documented, following a standardized format to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Field surveys are conducted to collect physical measurements and observations of the completed project.
- Existing plans and specifications are reviewed to verify compliance and identify discrepancies.
- Project records, including construction logs, change orders, and as-built markups, are meticulously examined.
- Collected data is documented in a clear and organized manner, ensuring all aspects of the project are accurately represented.
Verification and Validation Methods
Verification and validation are critical steps to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the as-built data. Various methods are employed, including field checks, comparing against existing plans, and cross-referencing with other data sources. This meticulous approach reduces errors and discrepancies.
- Field checks confirm the physical attributes of the project elements with the as-built drawings.
- Comparing the as-built drawings with the original design plans helps identify any deviations or discrepancies.
- Cross-referencing the as-built data with other project documentation, such as change orders and construction logs, ensures consistency.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing rigorous quality control measures is essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of the as-built services. This involves establishing clear standards, using standardized tools, and conducting thorough reviews at various stages of the process. Consistent application of these measures ensures a high-quality deliverable.
- Standards and checklists are developed to ensure consistent application of procedures.
- Using specialized software or tools for data entry and analysis enhances efficiency and accuracy.
- Regular reviews and audits of the as-built documentation by qualified personnel guarantee quality and completeness.
Flowchart of As-Built Service Process
A typical flowchart for an as-built service process starts with defining the scope and progresses through data gathering and documentation, followed by verification and validation. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the process, culminating in finalizing the as-built documents and their release to stakeholders.
The flowchart would visually represent the sequential steps, showing the branching and decision points in the process.
Benefits and Advantages
As-built services offer a plethora of advantages, significantly impacting project efficiency, cost, and risk management. These services provide a detailed and accurate representation of the completed project, enabling informed decision-making and future planning. By leveraging the insights from as-built data, organizations can streamline operations, optimize resource allocation, and minimize potential future issues.
Key Advantages of As-Built Services
As-built services provide a wealth of benefits across various aspects of a project. They allow for a comprehensive understanding of the final product, enabling informed decision-making and optimized resource utilization. This detailed record minimizes potential errors and discrepancies during future operations or modifications.
- Improved Efficiency: As-built documentation streamlines future operations and maintenance. For example, precise diagrams and specifications enable technicians to quickly locate components and perform repairs or upgrades, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency. Construction teams can use as-built drawings to better understand the existing structure and plan future projects more effectively.
- Cost Reduction: By providing clear and accurate information, as-built services can help prevent costly rework and errors during future projects. For instance, if an alteration or expansion is planned, the existing infrastructure’s specifications are available, reducing the risk of unforeseen issues and unexpected costs. Clear communication of project specifications and requirements minimizes rework.
- Risk Mitigation: As-built services provide a detailed record of the project, minimizing risks associated with future modifications or expansions. This detailed record allows for informed risk assessment and proactive mitigation strategies. For example, knowing the exact location of utilities and infrastructure avoids damage during future construction or maintenance work, reducing the risk of costly delays or accidents.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Accurate as-built data facilitates informed decision-making for future projects and operations. For example, engineers can use as-built models to analyze the structural integrity of the completed project, leading to more effective design choices in future projects and expansions. The information allows for more informed planning, design, and resource allocation for future endeavors.
Impact on Various Areas
As-built services have a positive impact across different project phases and disciplines. Their accuracy and completeness enhance the overall project outcome.
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Detailed drawings and specifications guide future construction phases. | Reduced rework, optimized resource allocation, and faster project completion. |
| Maintenance | The precise location of components allows for quick and efficient repairs. | Minimized downtime, reduced maintenance costs, and improved equipment longevity. |
| Modifications and Expansions | Accurate information prevents errors and reduces costs during alterations. | Faster project execution reduced risks and minimized unexpected expenses. |
| Design | As-built data informs design decisions for future projects. | Enhanced structural integrity, improved resource utilization, and reduced risk. |
Challenges and Considerations
Source: co.uk
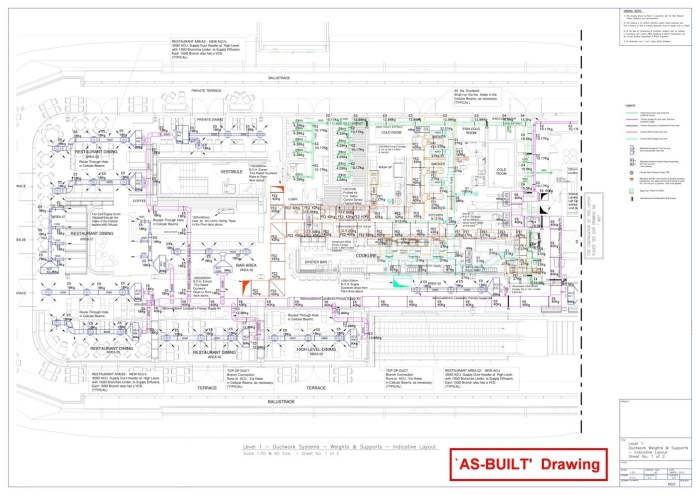
As-built services, while offering significant advantages, come with their own set of hurdles. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful implementation and avoiding potential pitfalls. Careful planning and proactive risk management are key to navigating these difficulties.
Implementing as-built services often involves navigating complex technical and logistical issues, and a thorough understanding of the potential challenges can help project teams tnticipate and mitigate them. Properly addressing these issues can lead to more efficient and cost-effective project delivery.
Potential Challenges
A variety of challenges can arise during the execution of as-built services. These challenges can stem from various sources, including communication breakdowns, data inconsistencies, and inadequate documentation. Addressing these challenges head-on is critical to ensure a successful outcome.
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: Inaccurate or incomplete data is a major obstacle in as-built services. Errors in the as-built documentation can lead to costly rework and delays. This is because incorrect information might affect the design, construction, or operation of the project.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration among various stakeholders, including engineers, contractors, and clients, are paramount. Misunderstandings or poor communication can lead to discrepancies and delays in the project. This is particularly true when dealing with multiple teams working on different aspects of the project. For example, if the design team doesn’t communicate changes to the construction team, there could be errors in the final product.
- Documentation Management: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation is crucial. Poor documentation management can lead to difficulties in accessing and using the as-built information, impacting project continuity. This is especially relevant when dealing with large and complex projects, where the volume of data can be overwhelming. A robust system for managing documents and revisions is essential.
- Technology Integration: Integrating as-built services with existing systems and technologies can be challenging. Compatibility issues, data format discrepancies, and lack of technical expertise can hinder the smooth operation of the system. Implementing the necessary technological infrastructure to support as-built services is often a critical aspect of the project.
Limitations and Constraints
As-built services are not without their limitations. Understanding these constraints is essential to realistic expectations and avoiding potential disappointments.
- Scope Limitations: As-built services may not cover all aspects of the project, particularly those that were not explicitly documented. There may be areas where the scope of the service needs to be clarified.
- Time Constraints: The time required for completing as-built services can be significant, depending on the project’s complexity and scale. This can lead to delays if not properly managed.
- Resource Constraints: As-built services may require significant resources, including personnel, technology, and funding. Resource constraints can impact the quality and timeliness of the service.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies, As-built services
Potential risks are inherent in any project, and as-built services are no exception. Identifying and mitigating these risks is crucial for successful project delivery.
- Data Inconsistency: Inconsistencies in data can lead to errors in the as-built model. This can be mitigated by implementing rigorous data validation procedures and using data quality tools.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements is critical. This can be addressed through meticulous review and adherence to established standards.
Importance of Accurate Data and Documentation
Accurate and complete data and documentation are essential for the success of as-built services. Without precise information, the entire process can be compromised.
- Ensuring Accuracy: Accuracy is vital for preventing errors in the as-built model. This can be achieved by implementing strict data validation procedures and using various quality control measures.
- Facilitating Communication: Clear documentation promotes better communication among stakeholders. This enhances understanding and reduces potential conflicts.
Common Challenges and Potential Solutions
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data Inconsistency | Discrepancies in data from different sources | Implement data validation procedures, use data quality tools, and establish clear data standards. |
| Communication Breakdown | Poor communication among stakeholders | Establish clear communication channels, hold regular meetings, and use project management tools. |
| Technology Integration Issues | Compatibility problems with existing systems | Thorough testing of compatibility, implementation of data migration strategies, and training on new technologies. |
| Documentation Gaps | Lack of complete or accurate documentation | Develop comprehensive documentation standards, implement version control systems, and encourage active documentation practices. |
Future Trends and Developments
As-built services are rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing industry needs. The future promises exciting developments, incorporating more sophisticated tools and approaches to improve accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of data. This section explores emerging trends, innovative applications, and potential future developments in as-built services.
The ongoing digitization of construction and infrastructure projects is significantly influencing the evolution of as-built services. Cloud-based platforms, BIM (Building Information Modeling) integration, and the rise of AI are creating opportunities for more comprehensive and automated as-built documentation. These technologies are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, creating new possibilities for how we manage and utilize as-built data.
Emerging Trends in As-Built Services
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of as-built services. These trends include increased automation, integration with other technologies, and a focus on data accessibility and usability. Automation through AI and machine learning is expected to play a critical role in automating data collection and analysis tasks. This automation will lead to greater efficiency and accuracy in the process.
Innovative Applications of As-Built Services
Innovative applications of as-built services are expanding beyond traditional infrastructure projects. These services are now being applied in areas like urban planning, facility management, and even in the analysis of historical buildings and sites. The use of as-built data in urban planning allows for more informed decision-making regarding infrastructure development and resource allocation.
Potential Future Developments
Future developments in as-built services are likely to focus on improved data visualization and analysis capabilities. The use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies is poised to revolutionize how as-built information is visualized and interacted with. Real-time updates and dynamic visualizations will enhance the understanding and management of construction projects.
Predictions of As-Built Services
As-built services are predicted to become more integral to the entire project lifecycle, from design and planning to construction and maintenance. Real-time data sharing and collaborative platforms will enable seamless communication and data exchange among stakeholders. This improved integration is expected to reduce project delays and improve overall project outcomes.
Possible Future Trends in As-Built Services
- Increased Automation: AI-powered tools will automate data collection, analysis, and reporting tasks, improving accuracy and reducing human error.
- Enhanced Data Visualization: Interactive dashboards and 3D models will provide clearer insights into as-built data, facilitating better understanding and decision-making.
- Integration with IoT Devices: As-built data will be enriched by real-time sensor data from IoT devices, enabling continuous monitoring and analysis of infrastructure performance.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based platforms will offer secure storage, access, and collaboration for as-built data, making it more accessible to stakeholders.
- AR/VR Applications: AR and VR technologies will revolutionize how as-built information is visualized and experienced, enabling immersive visualizations for stakeholders.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, as-built services are invaluable for ensuring projects meet specifications, minimizing risks, and facilitating future decision-making. By understanding their components, processes, and benefits, organizations can leverage this approach to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall project outcomes. The future of as-built services looks promising, with innovations poised to further expand its application and impact across diverse industries.